遗传力的概念和计算
前言
在作物育种过程中,通常会有多年多点的试验,这种试验通常叫做多环境试验(multi-environment trial,MET)。为了对MET进行准确的测量、最终实现实现MET的准确比较,育种学家通常会计算广义遗传力和狭义遗传力。这个文档主要有三个目的:
- 说清楚遗传力的概念;
- 展示使用合适的方法计算遗传力;
- 提供稳定的方法计算和比较田间试验的准确信。
遗传力的定义
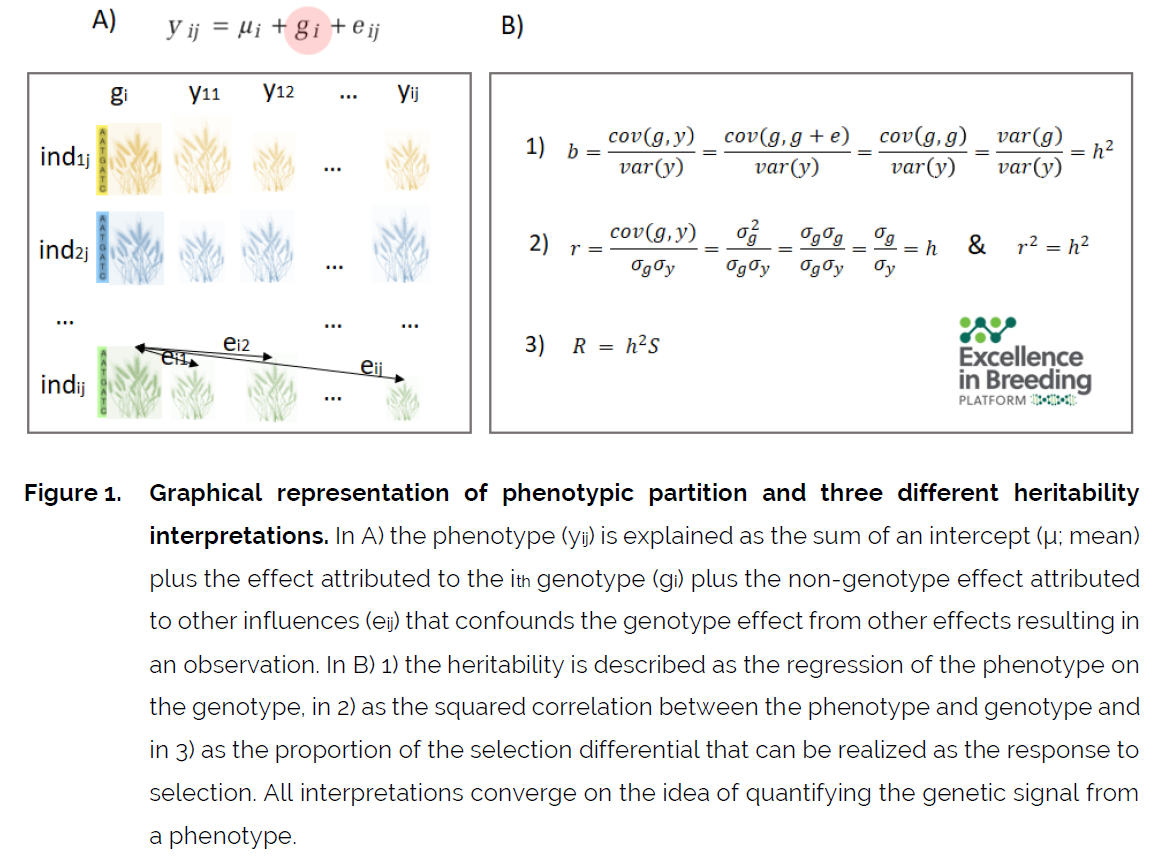
下图A中的公式表示表型可以用截距$\mui$加上第i 种基因型的效应加上其他的非基因型效应$e{ij}$,非基因型效应会影响基因型效应对表型的解释。
下图B就解释了什么什么是遗传力:
1)表型和基因型之间的回归关系;
2)表型和基因型之间的平方相关性;
3)被描述为选择差异中能够实现的选择反应的比例。
个人理解:基因型在表型决定过程中占了多大比例,也就是$gi$对$y{ij}$的大小的影响程度。
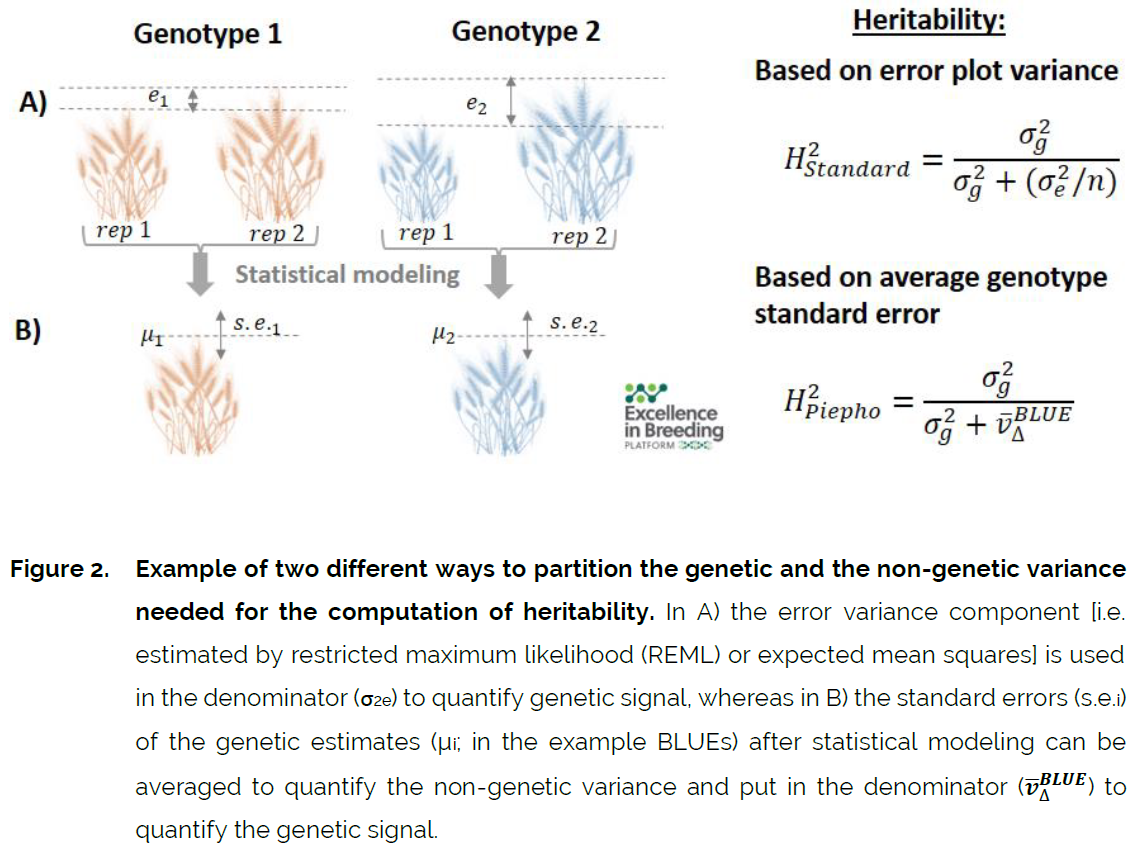
表型的方差可以分为两部分:
1)遗传方差:由遗传差异引起的表型方差;
2)误差方差:非遗传因素引起的表型方差,如环境引起的。
遗传力的误解
- A heritability of x indicates that x% of the trait is determined by genetics. 遗传力为0.4表示这个性状的表型变异中,有40%是由基因型的变异引起的;但是不能认为每个植株的性状表现有40%是基因决定了,其余部分是由其他因素影响决定的。
- A low heritability means that traits are not determined by genes. 只要遗传力的值大于0,就说明基因对表型有影响。遗传力是由遗传方差个表型方差的比例决定的。一个很低的遗传力只能说明遗传变异比表型变异更小。(例如,玉米的分枝在很大程度上是由遗传决定的,但由于现代玉米育种项目中使用的大多数基因型只有一个主茎,因此分枝的遗传方差非常低。)
- A low heritability means that genetic differences are small. 遗传力很低时并不能直接说是遗传变异很小,还有可能是误差变异很大,比如环境的影响巨大,遗传的影响较小。(例如,对某种感染的抵抗力将取决于抵御该感染的遗传潜力;问题在于如何测量这种潜力。如果仅对甜菜植物中的线虫感染进行一次田间测量,它只会记录当时感染的植物,但这可能会因选择的环境而影响感染水平的记录。)
- A heritability is a fixed value. 遗传力反映的是在一个特定的群体的表型变异中,遗传变异组分的相对权重。遗传力不仅取决于群体的遗传变异,还会受到环境和观测的准确度的影响。一个群体的遗传变异很可能和另外一个群体的遗传变异不同。而且,一个群体的遗传力会随时间发生变化。
- A high heritability implies a major-effect QTL. A major-QTL trait like eye color can have low heritability if the population scanned have only one type of eye color, or a high heritability of we observe all types of color. A highly quantitative trait like yield can have a high heritability is the experiment is well conducted with high appropriate replication levels, but can also have low heritability if the agronomic management is poor.
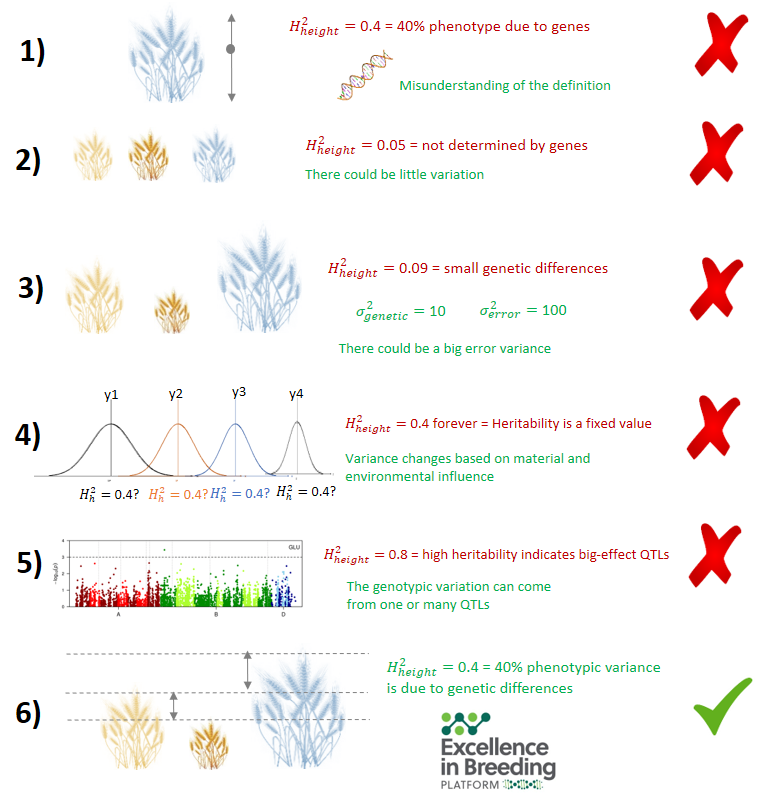
In 1), a misunderstanding of the concept results in the conclusion that a percentage of the phenotype is due to genes. In 2), the lack of variation resulting in low heritability is misunderstood to be consequence of no genetics contributing to the expression of the trait. In 3), a low heritability is misunderstood to reflect a small difference between genotypes when it could also be attributed to a large error variance. In 4), heritability is wrongly thought to be the always the same across time or populations. In 5), heritability is wrongly interpreted to be correlated to the number of large QTLs. In 6), the correct interpretation of heritability is provided.
遗传力的计算
Cullis等提出的广义遗传力计算方法
在这个公式中:
- $\sigma^2$表示方差;
- g表示基因型;
- $\bar{\nu}_{\triangle}^{BLUP}$表示基因型BLUPs的平均标准差。
这个公式的优点在于,它可以作为常规田间试验分析的一部分进行计算,能够处理不平衡的数据集,并利用随机变量的特性,例如方差成分的估计。
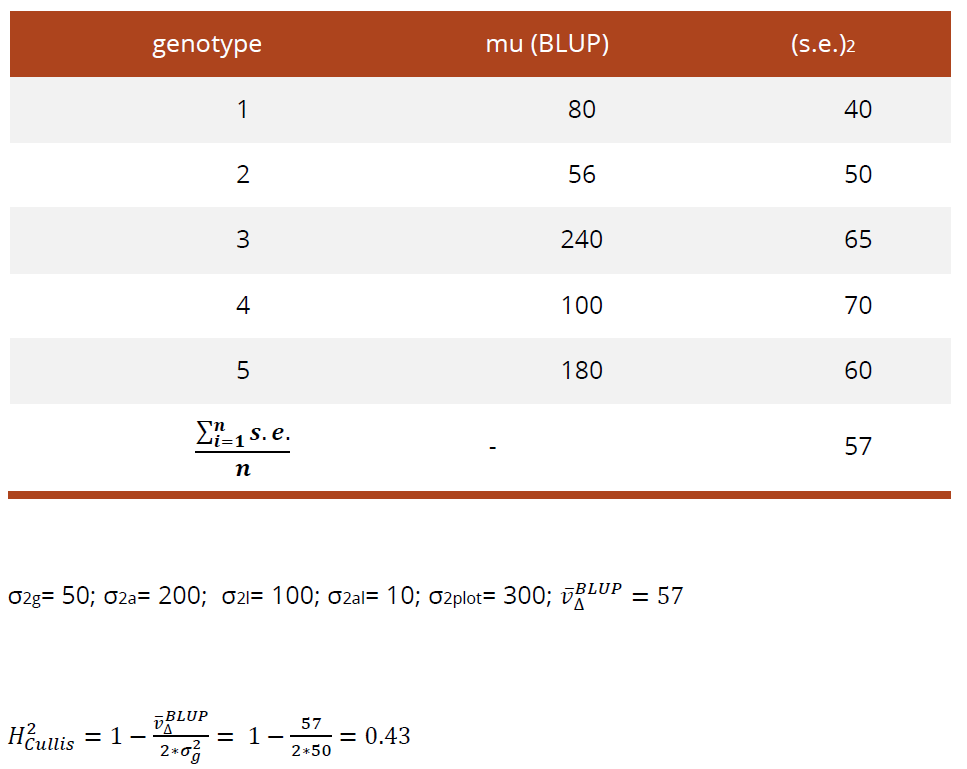
计算比较直接简单,但是需要每个个体都有2个及以上的重复,不然没法计算标准误。最后的结果0.43说明有43%的表型变异是由遗传差异引起的。
标准的广义遗传力计算方法
这种方法的优点在于计算简单且参数选择直观。缺点包括在数据不平衡时(在单一或多环境设置中,每个基因型的重复次数不同)可能会倾向于高估值,因为它假设数据集是平衡的。
其中${\sigmap^2 = \sigma_g^2 + \frac{\sigma{ga}^2}{\sigma{n_a}^2} + \frac{\sigma{gl}^2}{\sigma{n_l}^2} + \frac{\sigma{gal}^2}{\sigma{n_an_l}^2} + \frac{\sigma{plot}^2}{\sigma_{n_an_ln_r}^2}}$
在这个公式中:
- $\sigma^2$表示方差;
- g表示基因型;
- n表示重复数量;
- a表示年份;
- l表示地点;
- plot表示plot error.

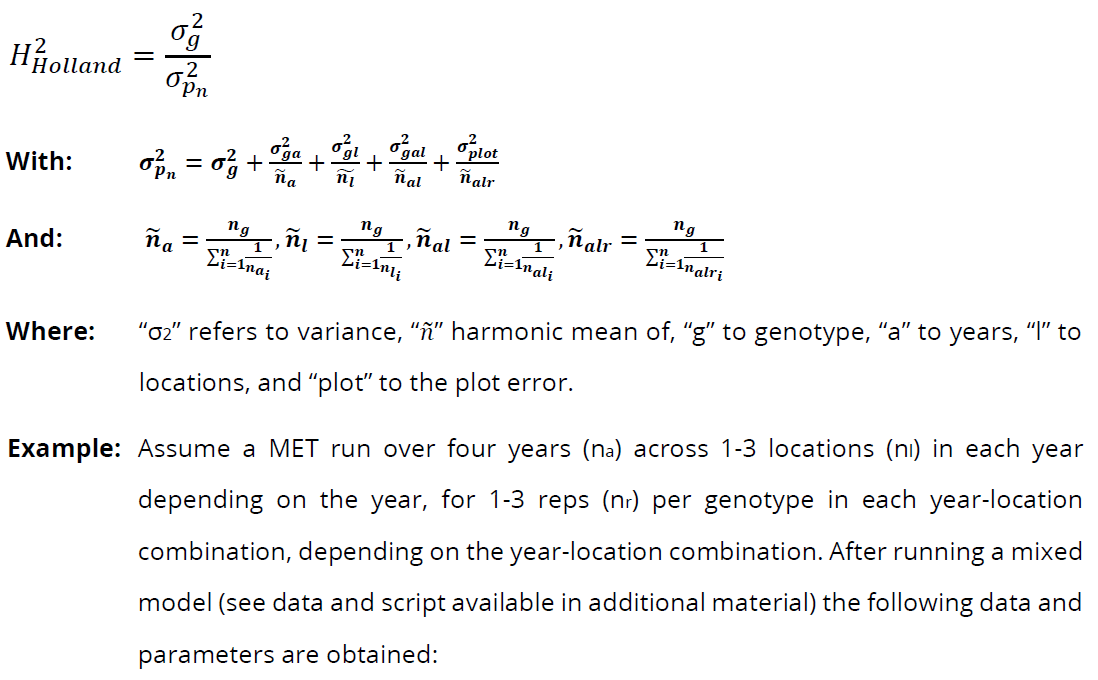
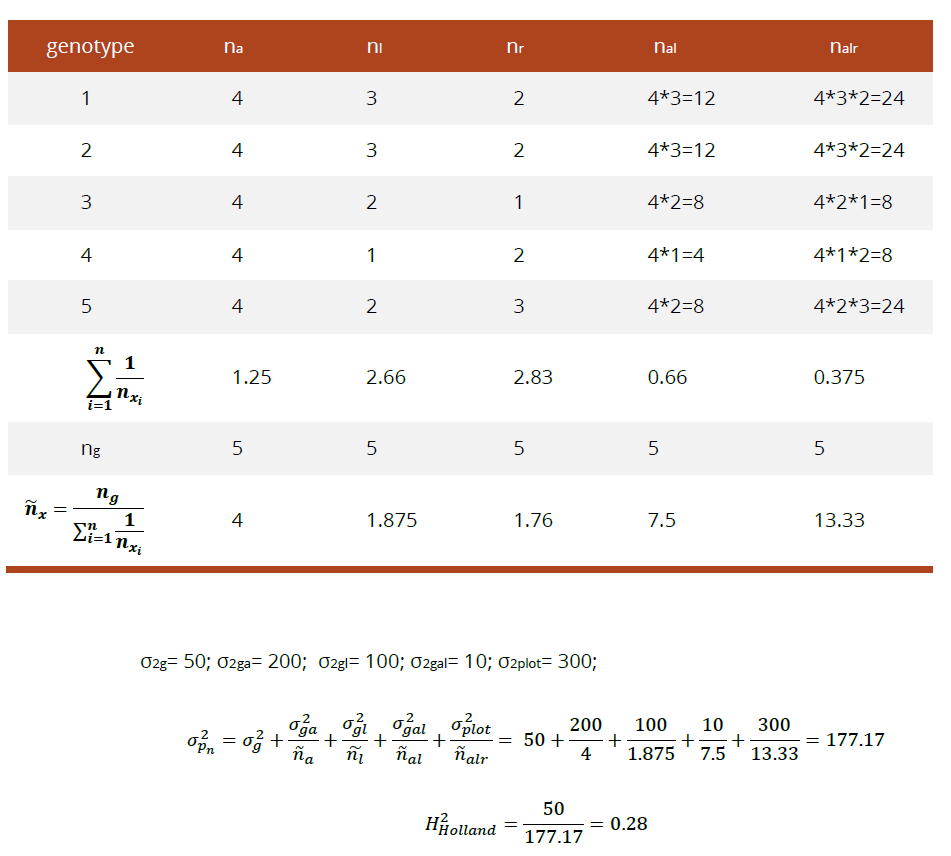
Ad hoc Holland广义遗传力计算方法
这个方法主要是解决重复数量不一样等问题。
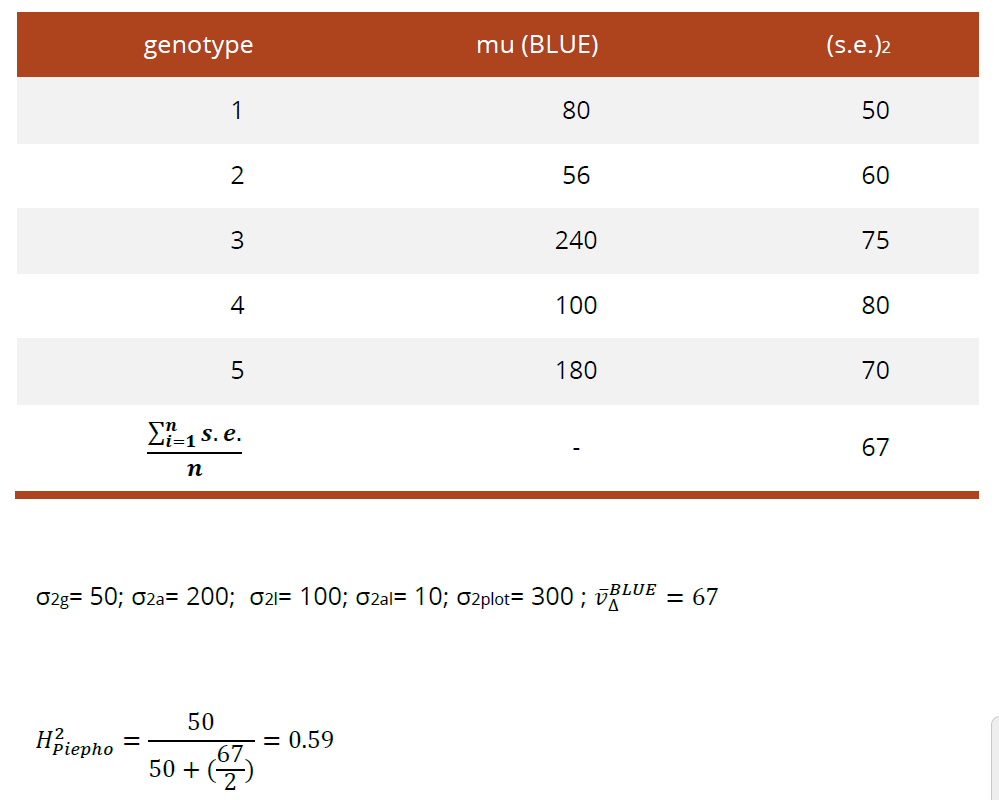
Piepho’s广义遗传力计算

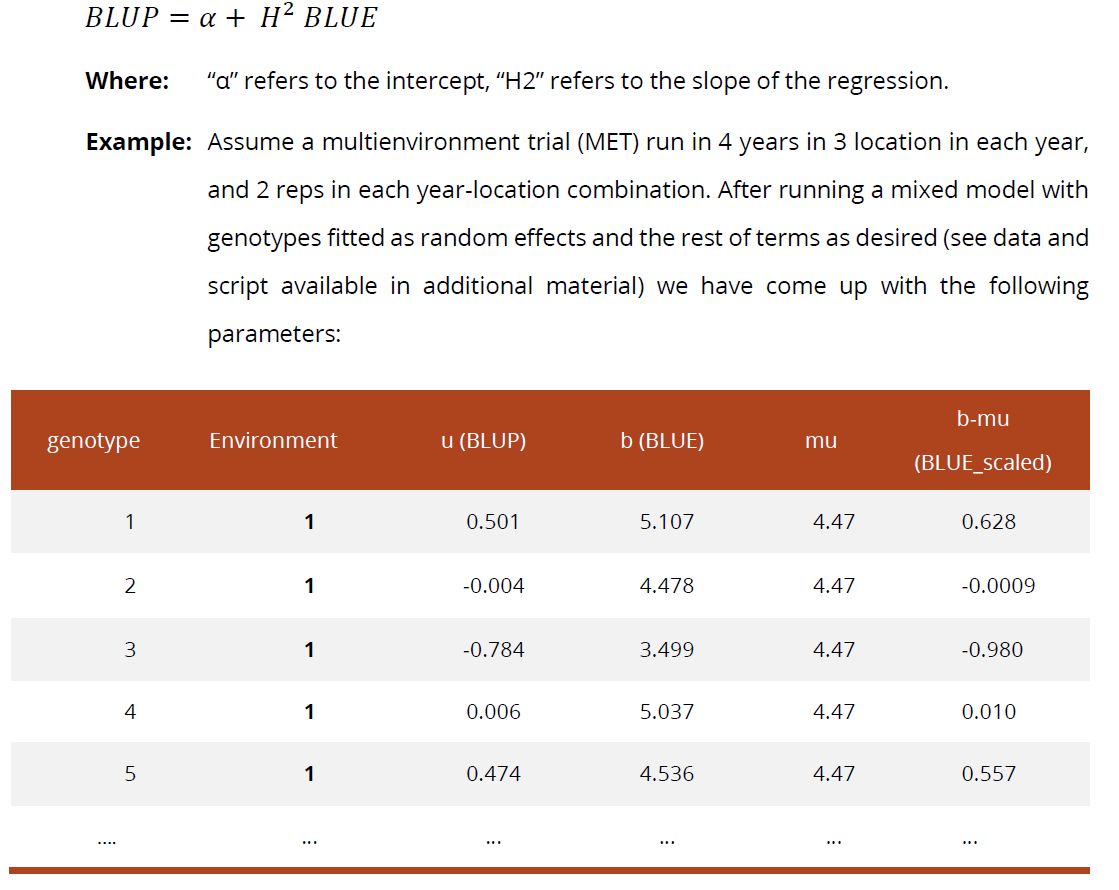
Walsh and Lynch广义遗传力计算
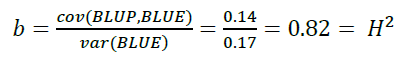
总结
This manual has set out the correct interpretation of heritability alongside some common misconceptions to be avoided. Additionally, an overview was provided of the features, advantages and disadvantages of some of the more robust heritability calculation methods in order to promote the adoption of common and transparent methods among breeding programs. Among those, the Cullis method (Cullis et al., 2006) was recommended as a robust method to account for unbalanced datasets. In addition, the Piepho and Walsh & Lynch methods are also considered robust but require additional considerations.